Housing laws in Texas have changed significantly in 2026. These updates affect renters, homeowners, landlords, and developers. Whether you are renting an apartment, buying a home, or managing property, understanding the changes is essential.
In this guide, we will cover key updates to eviction rules, tenant protections, landlord responsibilities, security deposit policies, and more. We will also explain what these laws mean for different groups and how they affect daily life.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of 2026 Housing Law Changes in Texas
Texas housing laws in 2026 focus on several important areas. Lawmakers aimed to balance tenant protections with property owner rights. They also sought to address housing affordability and development challenges.
Some major themes include:
-
Eviction law updates: Faster processes and clearer rules for both tenants and landlords.
-
Tenant rights protections: Strengthened fair housing rules and anti-discrimination measures.
-
Landlord responsibilities: More clarity on habitability standards and notice requirements.
-
Affordable housing and zoning: Changes to accommodate manufactured homes and higher-density projects.
-
Property tax and homestead exemptions: Adjustments that affect homeowners.
These changes are meant to make the housing market more transparent and fair. They also help prevent disputes and reduce legal confusion.
Key Legal Themes at a Glance
| Theme | What It Means | Who Is Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Eviction law updates | Faster hearings, limited counterclaims | Renters, landlords |
| Tenant protections | Anti-discrimination enforcement, fair housing rights | Renters |
| Landlord duties | Clearer notice rules, habitability requirements | Landlords, tenants |
| Affordable housing & zoning | Expanded manufactured housing options, ADUs allowed | Developers, property owners |
| Tax exemptions | Increased homestead exemptions | Homeowners |
Each of these changes has practical effects. For instance, renters now have less time to respond to eviction notices, but they also have clearer rights if they are being discriminated against. Landlords need to follow stricter procedures but benefit from faster resolution of disputes.
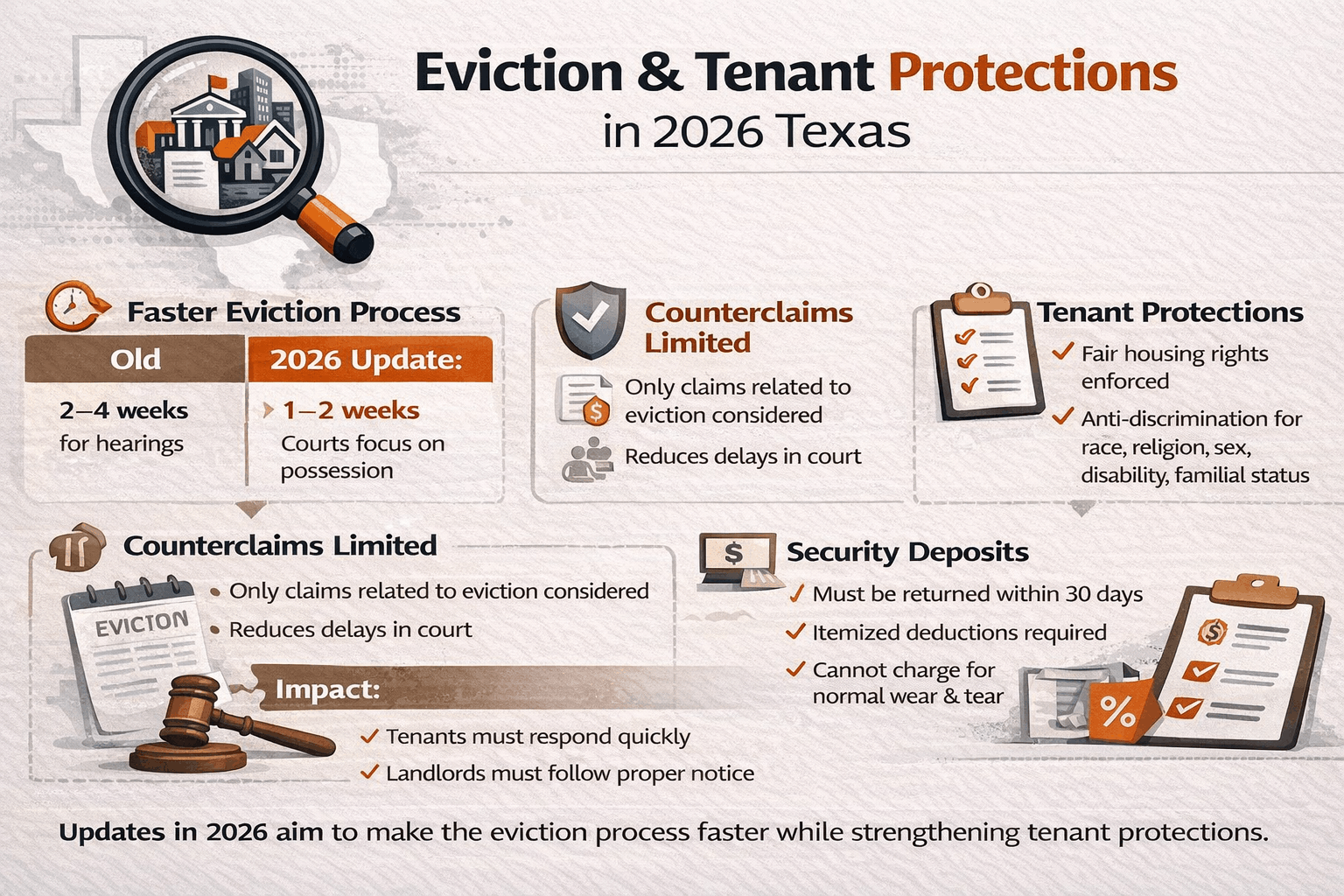
Eviction Law Changes in 2026
Eviction laws SB 38 and SB 1333 have been revised to make the process faster and more straightforward. The goal is to reduce delays in court and make outcomes clearer for both tenants and landlords.
Faster Eviction Proceedings
Under the 2026 updates:
-
Courts primarily focus on possession of the property.
-
Counterclaims unrelated to eviction are limited.
-
Timeline for hearings has been shortened.
This means landlords can move cases forward faster. At the same time, tenants need to act quickly if they want to challenge an eviction.
| Eviction Step | Old Law | 2026 Update |
|---|---|---|
| Filing notice | 3-day notice required | 3-day notice remains, but courts schedule hearings faster |
| Court timeline | 2–4 weeks | 1–2 weeks in most cases |
| Tenant defense | Broad counterclaims allowed | Only relevant claims considered |
The changes make the process more efficient. Tenants must respond quickly and gather documentation to support their case. Landlords should follow notice rules carefully to avoid delays.
Impact on Renters
-
Tenants have less time to file responses.
-
Legal defenses must be specific to the eviction reason.
-
Documentation of payments, maintenance requests, and communications becomes critical.
Impact on Landlords
-
Evictions for non-payment can be processed faster.
-
Proper notice and paperwork are essential.
-
Accurate records of lease agreements and communications help protect against disputes.
Eviction laws are only one part of the 2026 updates. Tenants still have rights, and landlords have responsibilities. Understanding both sides is key to preventing legal problems.
Squatter Laws and Unauthorized Occupants
Squatter laws clarify who has legal rights to a property and what procedures are required for removal. The 2026 changes separate squatters from holdover tenants, giving property owners clearer options.
Understanding the Difference
| Occupant Type | Definition | Removal Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Legal tenant | Signed lease, paying rent | Standard eviction process |
| Holdover tenant | Lease expired but continues to occupy | Eviction notice + court filing |
| Squatter | No legal right, occupies property unlawfully | Simplified legal removal |
Procedures for Property Owners
-
Property owners can file claims specifically for unauthorized occupants.
-
Law enforcement can assist in some cases.
-
Documentation of ownership and prior notices is essential.
Why It Matters
These laws prevent confusion about who can legally occupy a property. They also protect property owners from long delays in removing unauthorized residents. At the same time, tenants and others must understand their rights to avoid disputes.
Tenant Rights Under 2026 Texas Housing Laws
Tenants in Texas still have strong legal protections under the 2026 updates. These laws ensure fair treatment and prevent discrimination. Understanding these rights helps renters avoid unnecessary conflicts and assert themselves when issues arise.
Fair Housing Protections
Fair housing laws protect tenants from discrimination. Both federal and Texas laws prohibit housing discrimination based on specific characteristics.
Key protections include:
-
Race, color, and national origin
-
Religion and sex
-
Familial status (children in the household)
-
Disability (including reasonable accommodations)
These protections apply to rental applications, lease agreements, and day-to-day management by landlords. For example, landlords cannot refuse an application because the tenant has children or requires a service animal.
Reasonable Accommodations for Disabilities
Tenants with disabilities may request modifications to their living space. Landlords must consider these requests carefully. Examples include:
-
Installing ramps or grab bars
-
Allowing service animals or emotional support animals
-
Adjusting lease terms for accessibility needs
Landlords cannot charge extra fees for reasonable accommodations. Tenants should provide written requests and documentation when required.
Retaliation Protections
It is illegal for landlords to retaliate against tenants for exercising their rights. For instance, a landlord cannot increase rent or issue eviction threats because a tenant filed a maintenance complaint or reported a violation.
Security Deposit Rules and Application Requirements
Security deposits are an essential part of renting. The 2026 updates clarify how landlords can handle deposits and application fees.
Updated Security Deposit Guidelines
Security deposits are refundable payments meant to cover damages or unpaid rent. Key points under 2026 law:
-
Non-refundable fees (like application fees) must be clearly labeled.
-
Landlords cannot keep deposits for normal wear and tear.
-
Itemized deductions must be provided if any amount is withheld.
Table: Security Deposit Rules at a Glance
| Rule | Requirement | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Refund timeline | Must return within 30 days of lease end | 30 days |
| Itemized deductions | Required if deposit is withheld | 30 days |
| Non-refundable fees | Must be disclosed in writing | At application |
| Normal wear & tear | Cannot be charged | Always |
Rental Application Transparency
Application processes must be fair and transparent. Landlords should:
-
Disclose criteria for approval clearly
-
Avoid discriminatory questions
-
Handle application fees consistently
These changes protect tenants from unfair practices and ensure transparency in rental agreements.
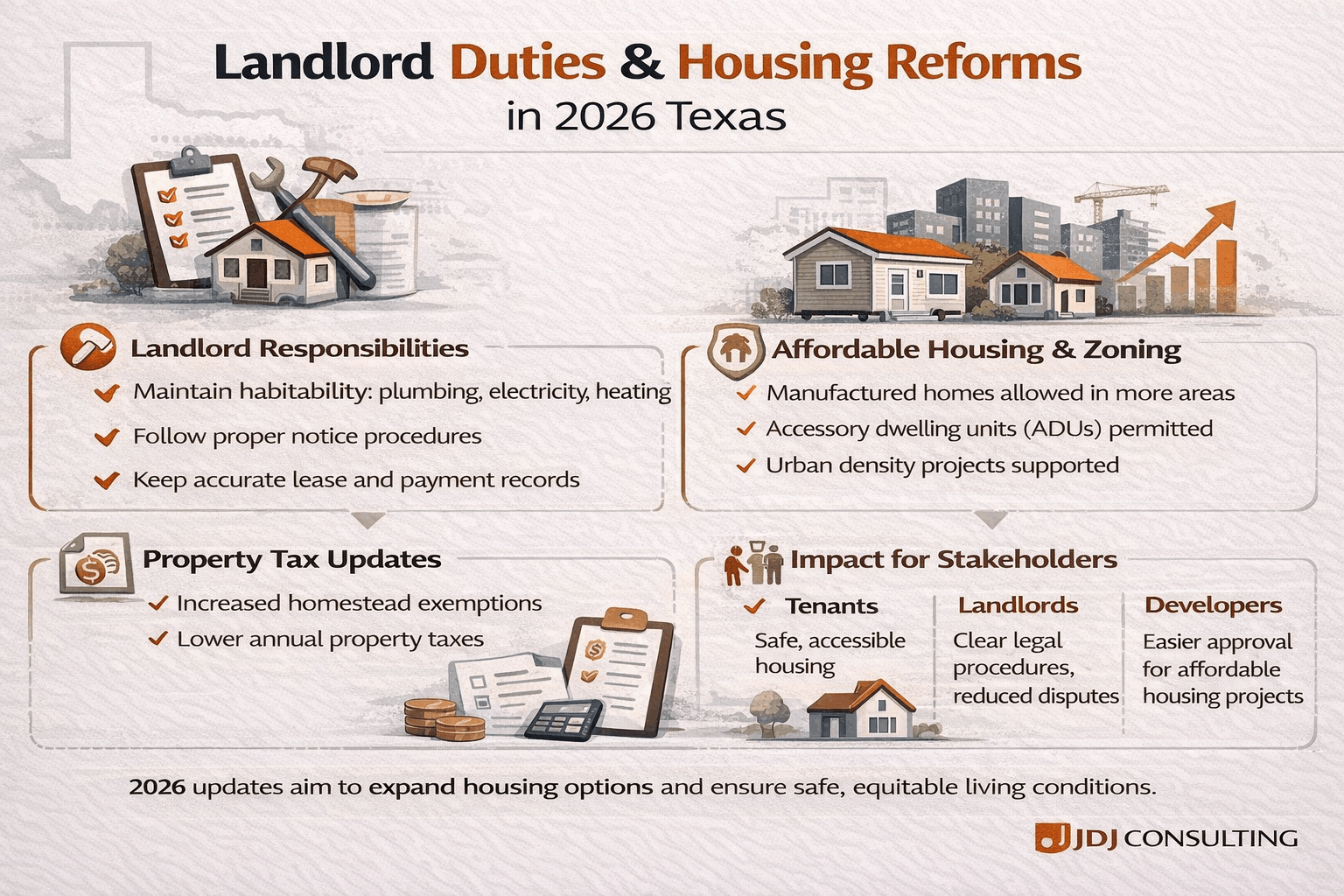
Landlord Responsibilities in 2026
Landlords have clear responsibilities under the new laws. Following these rules helps prevent disputes and ensures a safe, habitable environment.
Habitability Standards
Landlords must provide a safe and livable space. This includes:
-
Working plumbing, electricity, and heating
-
Structurally safe premises
-
Adequate sanitation and pest control
If these standards are not met, tenants can request repairs and, in some cases, withhold rent until the issues are resolved legally.
Notice Requirements
Landlords must follow strict notice rules for various actions:
-
Non-payment of rent: Written notice specifying the overdue amount.
-
Lease violations: Written warning with a chance to correct the issue.
-
Lease termination: Proper notice before filing eviction.
Failing to provide proper notice can delay legal proceedings.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
Proper documentation protects landlords in case of disputes. Key items to track:
-
Lease agreements and signed addendums
-
Maintenance and repair requests
-
Rent payments and receipts
-
Communication with tenants
Keeping organized records ensures landlords can demonstrate compliance with all laws and avoid costly legal challenges.
Affordable Housing and Zoning Reform in 2026
Texas housing laws in 2026 include significant updates to zoning and affordable housing policies. These changes aim to make more housing available and support both renters and developers.
Manufactured Housing Expansion
One major update affects manufactured homes. Cities are now required to allow HUD-certified manufactured homes in more areas. This makes affordable housing more accessible and offers homeowners alternative options.
Key points for manufactured housing:
-
Reduced local restrictions in many cities
-
Homes must meet federal HUD standards
-
Easier permitting process for builders
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs)
Accessory dwelling units, or small secondary homes on existing lots, are now encouraged in certain areas. These units can provide rental income for homeowners and increase housing supply.
-
Homeowners can build small units in addition to the main house
-
ADUs must comply with safety codes and zoning rules
-
Cities may limit the size and number of units per lot
Urban Density and Apartment Development
High-density housing is a focus in urban areas. Lawmakers aim to reduce the housing shortage by allowing more apartment buildings and multi-family units.
-
Some suburban cities are pushing back on density increases
-
Developers may benefit from state incentives for affordable housing
-
Balancing community concerns with housing needs remains a challenge
Table: Affordable Housing Changes in 2026
| Reform | What Changed | Who It Affects |
|---|---|---|
| Manufactured housing | Cities must allow HUD-certified homes | Developers, renters, homeowners |
| Accessory dwelling units | Secondary units allowed in more zones | Homeowners, tenants |
| Urban density | Easier approval for apartments | Developers, city planners |
These reforms aim to create more housing options while balancing local zoning and safety requirements.
Property Tax and Homestead Exemption Updates
Texas homeowners benefit from updated property tax laws and expanded homestead exemptions in 2026. These updates reduce financial burdens and provide tax relief.
Homestead Exemption Increases
Homestead exemptions lower the taxable value of a home, reducing the amount homeowners pay in property taxes. In 2026:
-
Exemption amounts have increased for primary residences
-
Homeowners must apply to their local appraisal district
-
Certain eligibility rules still apply
Impact on Homeowners
The increased exemptions can lead to significant savings. For example:
-
Lower annual property tax payments
-
Reduced financial strain for middle-income families
-
Greater predictability in household budgets
Homeowners should review their exemption status and ensure all filings are current to take advantage of these benefits.
Source of Income and Voucher Discrimination Issues
Another area addressed in 2026 is source-of-income discrimination. This issue affects tenants using housing vouchers or other alternative income sources.
Current Legal Status in Texas
-
There is no statewide requirement for landlords to accept vouchers.
-
Federal law protects certain tenants from discrimination, but local ordinances may vary.
-
Landlords must be aware of any city-specific rules that apply.
Guidance for Landlords
-
Treat all applicants fairly, regardless of income source
-
Stay informed about local ordinances that may restrict discrimination
-
Keep written records of rental decisions to prevent disputes
These updates aim to ensure fairness in the rental market while balancing landlord and tenant interests.

How 2026 Laws Affect Real Estate Investors and Developers
The 2026 housing updates also impact investors and developers. Understanding these changes helps them plan projects, reduce risk, and take advantage of new opportunities.
Risk Management Considerations
Investors and developers must be aware of legal risks:
-
Faster evictions reduce non-payment risk but require strict compliance
-
Security deposit rules must be followed to avoid disputes
-
Zoning changes may affect project approvals
Proper legal guidance is essential to avoid costly mistakes and ensure compliance with state and local laws.
Development Opportunities
New laws also create opportunities:
-
Manufactured housing: Easier approval allows affordable projects
-
High-density housing: Urban apartment projects are more feasible
-
Accessory dwelling units: Small homes on existing lots can provide rental income
Table: 2026 Opportunities and Risks for Investors
| Area | Opportunity | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Manufactured housing | Affordable housing projects | Local resistance or delays |
| High-density apartments | Larger rental income | Community opposition |
| ADUs | Additional rental units | Compliance with zoning rules |
Investors and developers who stay informed can plan projects strategically and meet the growing housing demand.
Practical Legal Tips for Renters, Landlords, and Developers
Understanding the law is one thing, applying it effectively is another. Here are some practical tips for each group.
For Renters
-
Respond quickly to eviction notices
-
Keep a record of rent payments and communications
-
Report habitability issues in writing
-
Know your fair housing rights
Landlords
-
Update leases to reflect 2026 law changes
-
Track notices, repairs, and payments carefully
-
Avoid discriminatory practices in rental applications
-
Train property managers on legal updates
For Developers
-
Review local zoning and density regulations before starting projects
-
Stay informed on manufactured housing laws
-
Document compliance with building codes and permits
-
Plan for community engagement to reduce resistance
Following these tips helps all parties reduce conflicts and comply with the law efficiently.
Common Misconceptions About 2026 Texas Housing Laws
Despite the updates, many people still misunderstand the laws. Clarifying these myths can prevent unnecessary confusion.
Common Misconceptions:
-
“Tenants have no protections anymore.” – Tenants still have strong rights under fair housing and eviction law.
-
“Evictions are automatic.” – Courts still review each case, and tenants can raise legal defenses.
-
“Security deposits can be kept for any reason.” – Landlords must provide itemized deductions for any withheld amount.
-
“Cities control all zoning decisions.” – State law sets broad rules, though cities still manage some local ordinances.
Correcting these myths helps tenants, landlords, and investors act confidently and legally.
Conclusion: Staying Compliant With 2026 Texas Housing Laws
The 2026 housing laws in Texas bring clarity and change to renters, landlords, homeowners, and developers. Faster eviction procedures, expanded tenant protections, zoning reforms, and updated tax exemptions all play a role.
Key Takeaways:
-
Tenants: Know your rights and document communications.
-
Landlords: Follow notice rules, maintain habitability, and avoid discrimination.
-
Developers/Investors: Stay informed on zoning, manufactured housing, and density rules.
By understanding these laws, property owners and renters can prevent disputes, protect their investments, and make better housing decisions.
Call JDJ Consulting: For personalized guidance on 2026 Texas housing laws, lease agreements, or property management compliance, contact JDJ Consulting. Professional advice ensures you stay compliant and avoid legal issues.
-
Phone: (818) 793-5058
-
Email: sales@jdj-consulting.com
-
Contact Page: https://jdj-consulting.com/contact-us/
FAQs: 2026 Texas Housing Laws
What are the major changes in Texas housing laws for 2026?
In 2026, Texas housing laws focus on eviction procedures, tenant protections, landlord responsibilities, and zoning reforms. Key changes include:
-
Faster eviction hearings with limited counterclaims
-
Expanded tenant protections under fair housing laws
-
New rules for security deposits and rental applications
-
Manufactured housing expansion and accessory dwelling unit (ADU) allowances
-
Property tax and homestead exemption updates for homeowners
These changes aim to balance tenant rights with property owner responsibilities and improve housing availability.
How have eviction procedures changed in 2026 Texas law?
Eviction laws now prioritize possession disputes and streamline court timelines. Key updates:
-
Courts focus on possession rather than unrelated counterclaims
-
Eviction hearings can take 1–2 weeks instead of 2–4
-
Proper notice is required to avoid delays
Tenants must respond quickly and maintain documentation, while landlords must follow notice rules precisely to ensure lawful eviction.
What protections do tenants have under 2026 fair housing laws?
Tenants are protected against discrimination based on:
-
Race, color, national origin
-
Religion, sex, familial status
-
Disability or need for reasonable accommodations
Landlords must provide accessible housing, allow service animals, and cannot retaliate for complaints or legal rights exercised. Documentation and written requests help enforce these protections.
Can landlords charge for normal wear and tear on security deposits?
No. Landlords cannot deduct from security deposits for normal wear and tear. Charges must be for damages beyond ordinary use, such as:
-
Broken fixtures
-
Holes in walls
-
Excessive dirt or neglect
Landlords must provide itemized deductions within 30 days of lease termination.
How quickly must landlords return security deposits?
Landlords must return security deposits within 30 days of lease end. If any portion is withheld for damages, they must provide an itemized statement explaining the deductions. Following these rules ensures compliance and prevents disputes.
What is the difference between a tenant, holdover tenant, and squatter?
-
Tenant: Legally signed lease, paying rent
-
Holdover tenant: Lease expired but still occupies property
-
Squatter: No legal right to occupy property
Property owners have distinct legal procedures for each type. Squatters can be removed through simplified legal actions, while tenants require proper notice and legal filings.
What responsibilities do landlords have for habitability?
Landlords must maintain a safe and livable property, including:
-
Working plumbing, electricity, and heating
-
Structurally sound buildings
-
Adequate sanitation and pest control
Failure to meet these standards can allow tenants to request repairs or, in some cases, withhold rent legally.
Are landlords allowed to retaliate against tenants for complaints?
No. Landlords cannot retaliate if a tenant exercises legal rights, such as:
-
Filing maintenance requests
-
Reporting safety or building code violations
-
Exercising fair housing protections
Retaliation, including eviction threats or rent increases, is prohibited under Texas law.
What are accessory dwelling units (ADUs) and their legal status in 2026?
ADUs are small secondary homes on existing lots. In 2026, many cities encourage ADUs to expand housing availability. Homeowners must:
-
Follow zoning and building code requirements
-
Limit size and number according to local ordinances
-
Ensure safety and habitability standards are met
ADUs provide rental income and increase housing options.
How do the 2026 laws affect manufactured housing?
Manufactured homes meeting HUD standards can now be placed in more areas due to reduced local restrictions. Developers and homeowners benefit from:
-
Easier permitting
-
Increased affordable housing options
-
Expanded choices for renters and property buyers
What are the updates to property tax and homestead exemptions in 2026?
-
Homestead exemption amounts have increased for primary residences
-
Homeowners must apply through the local appraisal district
-
Savings reduce annual property taxes, especially for middle-income families
These changes lower financial burdens and improve predictability in household budgets.
Are landlords required to accept housing vouchers?
Currently, Texas does not require landlords to accept vouchers statewide. However:
-
Federal law prohibits discrimination based on source of income in some cases
-
Local ordinances may apply in certain cities
Landlords should review local rules and treat all applicants fairly to prevent legal issues.
How can tenants respond to an eviction notice under 2026 law?
Tenants should:
-
Respond promptly in writing
-
Gather documentation of rent payments and communications
-
Present legal defenses limited to the eviction reason
Quick action is critical, as court timelines are faster than before.
What documentation should landlords keep to comply with 2026 laws?
Landlords should track:
-
Signed lease agreements and addendums
-
Maintenance and repair requests
-
Rent payments and receipts
-
Notices and communications with tenants
Good records protect landlords in legal disputes and ensure compliance with eviction and habitability rules.
How do zoning reforms impact developers in 2026?
-
More areas allow manufactured housing and ADUs
-
Urban density laws ease construction of multi-family apartments
-
Suburban opposition may delay projects
Developers can plan projects strategically by understanding state laws and local ordinances.
Can tenants request modifications for disabilities?
Yes. Tenants with disabilities may request:
-
Ramps or accessibility features
-
Lease term adjustments
-
Permission for service or emotional support animals
Landlords must respond reasonably and cannot charge extra fees for these accommodations.
What is the timeline for eviction hearings under 2026 law?
Eviction hearings can occur within 1–2 weeks, compared to 2–4 weeks previously. Courts focus on possession disputes only. Both tenants and landlords must act quickly and follow notice rules.
How do 2026 laws affect high-density apartment construction?
Developers benefit from reduced zoning restrictions for apartments. This allows:
-
More units per lot
-
Easier approval for affordable housing projects
-
Opportunities to meet growing urban housing demand
Local resistance may still impact timelines.
What are the consequences if a landlord fails to return a security deposit?
-
Tenants may file a claim in small claims court
-
Landlords may owe the full deposit plus damages
-
Proper documentation and timely action help prevent disputes and legal penalties
How can tenants verify their rights under Texas housing laws?
-
Review lease agreements carefully
-
Understand 2026 eviction and security deposit rules
-
Consult resources like TDHCA for fair housing guidance
-
Keep written records of complaints and communications